Paired-Tag: Simultaneous Single-Cell Epigenomics and Transcriptomics
Paired-Tag is a groundbreaking multiomic technology that captures histone modifications and RNA expression from the same cell without computational integration. By directly linking chromatin state to transcriptional output on a cell-by-cell basis, Paired-Tag unlocks mechanistic insights into cellular identity, developmental trajectories, and disease states that separate assays cannot reveal.
What Is Paired-Tag?
Paired-Tag is a single-cell multiomic library preparation method that simultaneously captures RNA expression and epigenetic marks—such as histone modifications, transcription factor binding, or chromatin-associated proteins—from the same individual nucleus. By integrating these two critical layers of gene regulation in one assay, Paired-Tag provides unprecedented resolution into how chromatin state drives cellular behavior.
Core Innovation
Unlike traditional multiome workflows that profile RNA and chromatin from different cells or require computational integration, Paired-Tag captures both modalities simultaneously from the identical nucleus. This eliminates batch effects, computational artifacts, and uncertainty—delivering direct, ground-truth relationships between chromatin accessibility/histone state and transcriptional output.
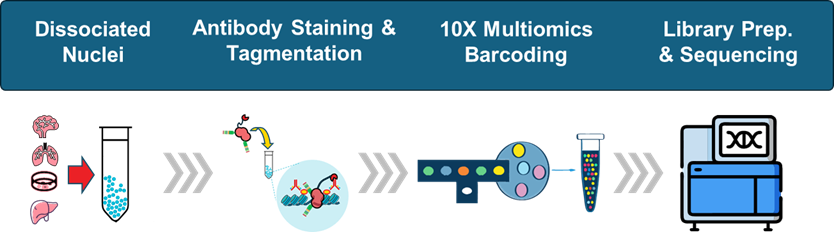
How Paired-Tag Works
-
Sample Preparation
Fresh or frozen tissue, organoids, PBMCs, or cell lines are processed into nuclei. Works efficiently on diverse sample types and tissues without requiring extensive optimization.
-
Dual Capture
Nuclei are simultaneously tagged with antibodies against histone modifications and barcoded oligonucleotides that capture RNA. Both capture events occur in the same nucleus without competition or interference.
-
Single-Cell Barcoding
Compatible with 10x Chromium Multiome - and soon other single-cell paltforms. Each nucleus is encapsulated with a unique barcode that identifies both the histone mark and RNA molecules from that cell.
-
Sequencing & Analysis
Dual FASTQ files (one for chromatin tags, one for RNA) are generated. Analysis produces linked cell-by-peak matrices and cell-by-gene matrices that can be directly correlated, revealing direct chromatin-transcript associations.
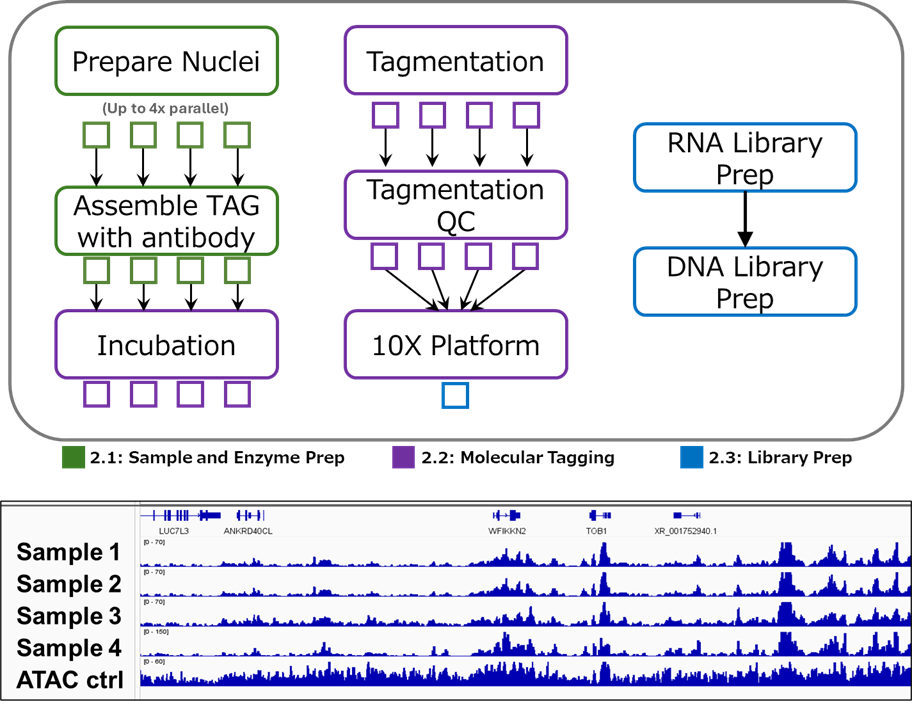
Multiplex Options
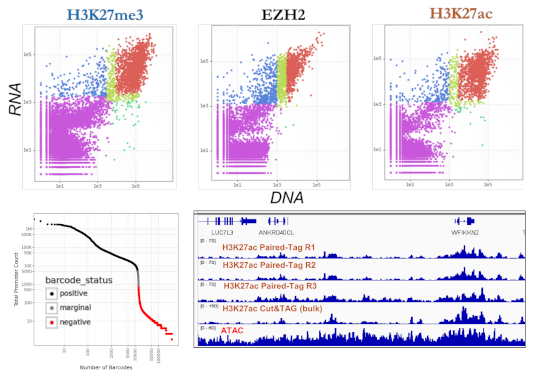
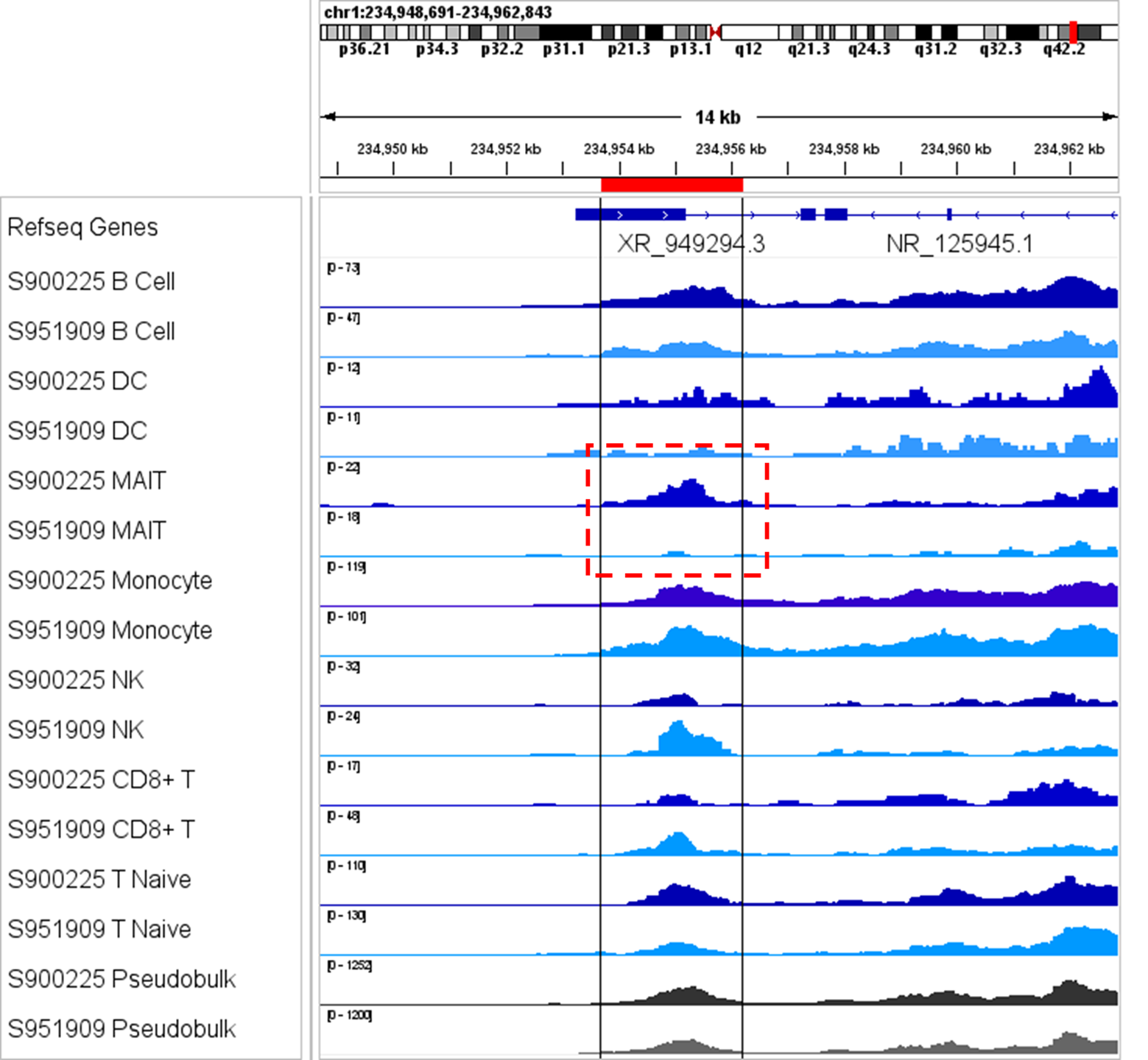
Data Highlights

Need assistance? Speak with a scientist to discuss platform compatibility and optimization.
Strengths and Capabilities of Paired-Tag
1. Joint Single-Cell Profiling
Paired-Tag captures histone modifications such as H3K27ac, H3K4me1, H3K27me3, and other marks alongside full transcriptomes in the same nucleus. This eliminates the computational burden and uncertainty of integrating separate assays—you have ground-truth chromatin-to-transcript linkage.
- Direct correlation without post-hoc integration algorithms
- No batch effects between modalities
- Reveals which genes are active when specific marks are present
2. Cell-Type Resolution and Rare Cell Detection
Paired-Tag discriminates diverse cell types and states in heterogeneous tissues by clustering on simultaneous epigenomic and transcriptomic signatures. RNA-based cell-type annotation combined with epigenetic characterization enables discovery of rare and transitional populations without FACS or enrichment.
- RNA clustering identifies cell types; epigenetics characterizes regulatory states
- No sorting bias; all cell types profiled equally
- Reveal rare populations invisible in bulk workflows
3. High-Throughput and Deep Coverage
Paired-Tag generates tens of thousands of unique chromatin loci and thousands of RNA UMIs per nucleus. Recent droplet implementations scale to profile hundreds of thousands of cells in a single experiment, enabling comprehensive atlases of complex tissues.
- 10K–20K cells per sample on standard platforms
- 15K–25K cells/lane with multiplexing (high-throughput cohorts)
- Deep per-cell coverage for robust peak/gene calling
4. Versatile Sample Compatibility
Works efficiently on fresh or frozen tissue, organoids, PBMCs, cell lines, and other sample types. This versatility makes Paired-Tag practical for translational studies, clinical cohorts, and archived sample analysis.
- Fresh and frozen samples
- FFPE-compatible protocols available
- Minimal sample optimization required
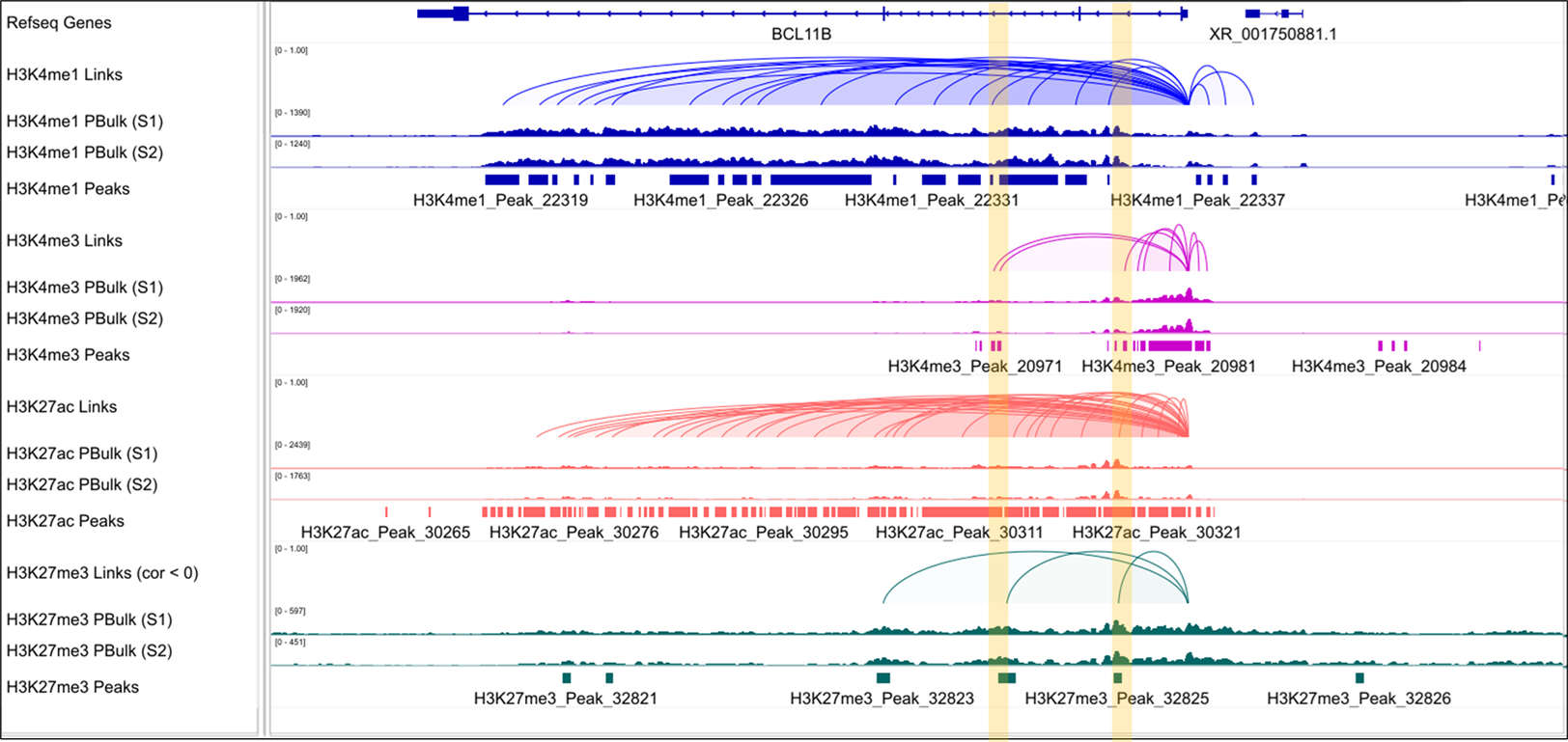
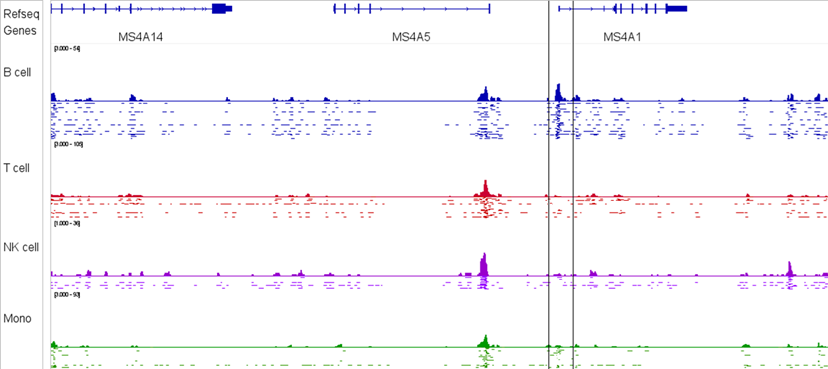
Research Applications
Developmental Biology
Track chromatin remodeling and gene expression changes during cell-state transitions and differentiation pathways. Identify epigenetic drivers of developmental decisions.
- Cell-fate specification mechanisms
- Epigenetic priming during lineage commitment
- Transcription factor activity linked to enhancer activation
Cancer Biology & Immunology
Link enhancer activation to tumor heterogeneity, immune evasion, and treatment resistance. Characterize T cell exhaustion, CAR-T functionality, and immune cell states.
- Tumor-associated macrophage epigenetics
- T cell exhaustion and recovery programs
- Treatment response epigenetic signatures
Disease Mechanism & Biomarker Discovery
Combine transcriptomics and epigenetics for mechanistic insights into disease pathogenesis. Identify epigenetic dysregulation underlying disease states and candidate therapeutic targets.
- Neurodegeneration and aging
- Autoimmune dysregulation
- Metabolic disease and diabetes
Perturbation Studies & Validation
Measure on-target chromatin effects and off-target transcriptional impacts of CRISPR, degraders, or compounds. Validate drug targets with dual-modality readouts.
- CRISPR screen validation
- Compound mechanism of action
- Chromatin remodeler targeting
Environmental Toxicology & Exposure Science
Paired-Tag reveals how environmental exposures—such as air pollution, e-cigarette aerosols, or chemical stressors—alter epigenetic landscapes and disrupt gene regulation. By directly linking chromatin changes to transcriptomic dysregulation, it elucidates molecular pathways sensitive to environmental stressors and potential long-term health impacts.
- Cell-type-specific epigenetic vulnerabilities
- Gene regulatory network disruption
- Recovery and adaptation mechanisms
Research Highlights
Pancreatic Islet Cell Heterogeneity in Diabetes
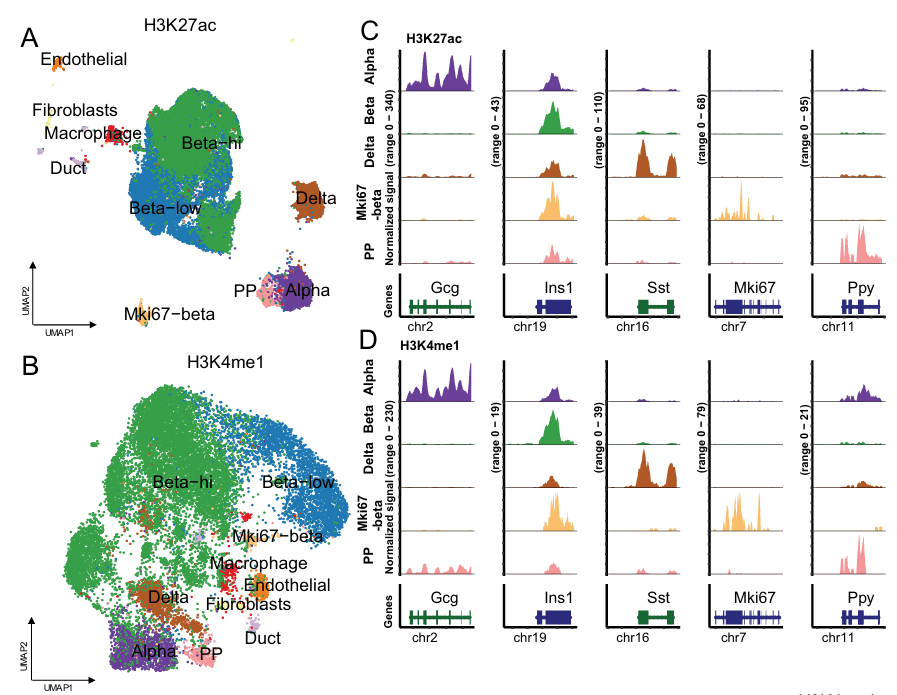
Paired-Tag profiling of pancreatic islets has revealed novel insights into β-cell heterogeneity and stress responses directly relevant to diabetes pathogenesis. The assay uncovered distinct β-cell subtypes derived from biochemically and epigenetically defined progenitors, demonstrating how histone modification patterns and epigenetic dosage shape functional specialization in insulin-secreting cells.
- Identified β-cell subtypes with distinct epigenetic and transcriptional signatures
- Mapped epigenetic dysregulation underlying β-cell stress during autoimmune attack in Type 1 diabetes
- Revealed regulatory networks far more detailed than bulk approaches
- Advanced target identification for therapeutic intervention
Prenatal E-Cigarette Exposure and Brain Development
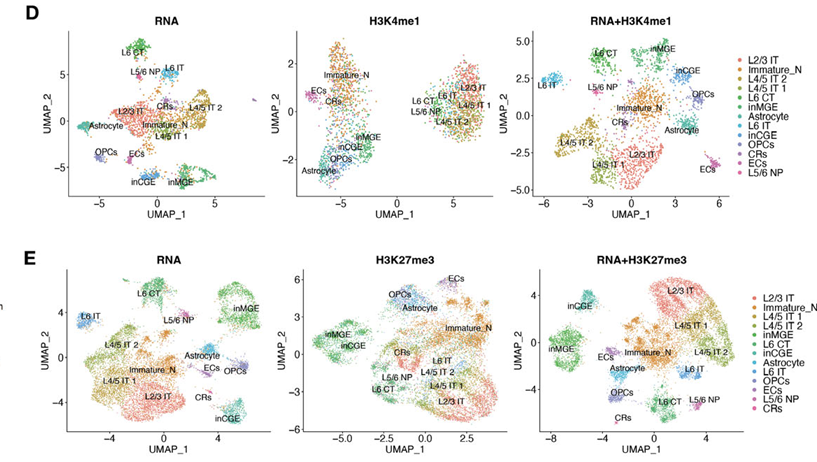
A recent study applying Paired-Tag to the prenatal mouse brain exposed to e-cigarette aerosols delineated the epigenetic consequences of environmental exposure on neurodevelopment. The assay revealed altered histone modification landscapes at enhancer and promoter regions within excitatory neurons and glia, associated with disrupted gene expression programs critical for brain development.
- Mapped cell-type-specific epigenetic vulnerabilities to prenatal exposures
- Linked chromatin changes directly to transcriptomic dysregulation
- Identified molecular pathways mediating environmental toxin impact
- Revealed mechanistic basis for potential long-term neurodevelopmental impairments
Why These Results Matter
These case studies exemplify the transformative power of Paired-Tag:
- Direct mechanistic insights: By linking epigenetic marks to gene expression in the same cell, researchers discover regulatory relationships invisible in separate assays.
- Disease-relevant discoveries: Cell-type and state-specific epigenetic dysregulation—the hallmark of disease—is captured with unprecedented detail.
- Therapeutic targets: Integrated epigenetic-transcriptomic data accelerates identification of druggable pathways.
- Precision medicine: Paired-Tag enables personalized profiling of patient samples for therapeutic response prediction.
Transform Your Epigenetic Research
Paired-Tag represents a paradigm shift in single-cell multi-omics. By directly linking chromatin state to transcriptional output from the same cell, Paired-Tag enables mechanistic discoveries that computational integration cannot achieve. Whether you're exploring fundamental biology or translating findings into precision medicine, Paired-Tag delivers the insights you need.